What Are Electromagnetic Clutches and Electromagnetic Brakes?
Their Types and Structures
What Are Electromagnetic Clutches and Electromagnetic Brakes?
Electromagnetic clutches and electromagnetic brakes are devices that control power and rotary movement using an electromagnetic force generated by energizing coils. Clutches connect and disconnect with power while brakes brake and maintain rotary movement. It is possible to divide these into electromagnetic actuated types and spring actuated types depending on that method of operation.
We have described these electromagnetic clutches and brakes in detail below. Clutches, brakes and other mechanical parts are also used in bicycles and cars in general. Therefore, you probably see them everywhere on a daily basis.
Nevertheless, although we simply say clutches and brakes, in fact, there are various types. We can broadly divide them into mechanical clutches and brakes, hydraulic clutches and brakes, pneumatic clutches and brakes, and electromagnetic clutches and brakes. These operate and use clutches and brakes mechanically, hydraulically, pneumatically and electromagnetically as their names suggest.
Electromagnetic clutches and brakes that operate with an electromagnetic force are used for industrial purposes and are most frequently used in general among these types.
Such industrial clutches and brakes are often embedded and used in machines, devices and other products. Therefore, there are not many opportunities to see them being used directly. Nevertheless, they play an extremely important role in controlling the power of various machines.
We explain in detail below about these electromagnetic clutches and brakes.
INDEX
What Are Electromagnetic Clutches?
What Are Electromagnetic Brakes?
Electromagnetic clutches and brakes and mechanical elements that control power using an electromagnetic force. They are often collectively called clutches and brakes because their operating principles are very similar. However, their roles are completely different. We give the roles of each below.
Role of Electromagnetic Brakes: To Stop Power
Electromagnetic brakes are a mechanical element to stop power. They are able to stop/maintain and slow down various movements with an electromagnetic force. In fact, they are often used in the lifting mechanisms of articles being transported.
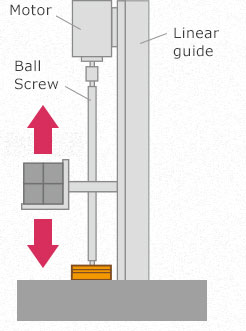
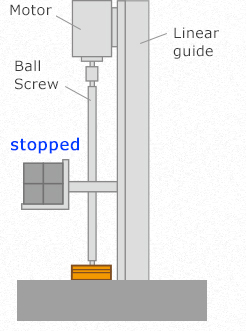
As you can see in the figure below, a brake is used when raising the transportation unit to a certain position or when stopping it at a fixed position.
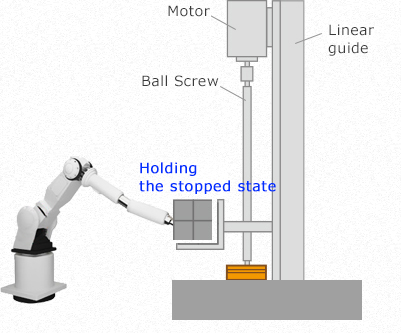
In addition to the above roles, electromagnetic brakes also have the role of maintaining a stopped state. Maintaining is a function to ensure that a machine or device does not move from the location where it has been stopped. For example, in the figure below, the brake is being used to continuously maintain the lifting platform in a fixed position during work in which a robot is placing articles to be transported on a lifting platform.
Role of Electromagnetic Clutches: To Transmit and Cut Off Power
Electromagnetic clutches are a mechanical element to transmit and cut power on the driven side with an electromagnetic force. Put simply, they can disconnect and connect power without stopping the power.
The operations and roles of electromagnetic clutches are harder to understand than those of electromagnetic brakes. Therefore, please first watch the video below.
How are clutches used? For example, as shown in the figure below, they can convey or cut power from the motor to the conveyor without stopping the power (without turning off the motor) by being mounted between the motor and conveyor (load).
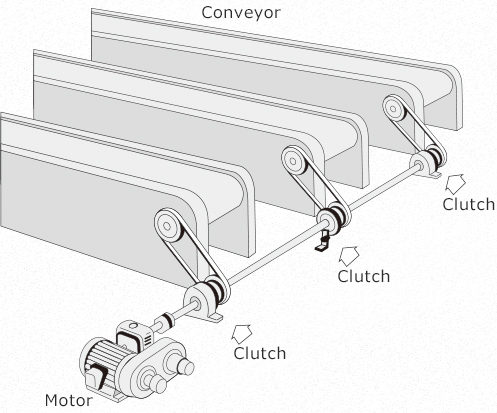
- Summary 1: Role of Brakes
- ・To stop/maintain or slow down power
- Summary 2: Role of Clutches
- ・To transmit or cut off power
Next, let’s look at what types of clutches and brakes are available.
Types of Electromagnetic Clutches
and Electromagnetic Brakes
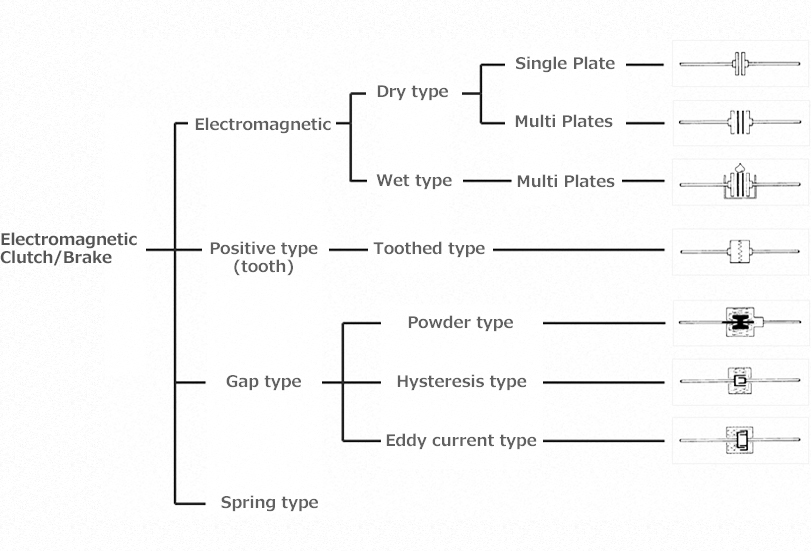
Electromagnetic clutch and brake systems include friction types, engagement types, gap types and spring types. These are categorized by the method used to generate torque. Each type has its advantages. This means that they must be used according to the application.
Of these, the most widely used for industrial purposes is friction types with their simple structure, inexpensiveness and excellent controllability. Torque is generated by pressing together friction materials.
Miki Pulley mainly handles these friction type. However, we also handle engagement type tooth clutches and spring type spring actuated brakes. We will now explain the strengths of each type with a focus on the clutches and brakes we handle.
Types of Electromagnetic Clutches and Brakes
of Miki Pulley
Types of Electromagnetic Brakes
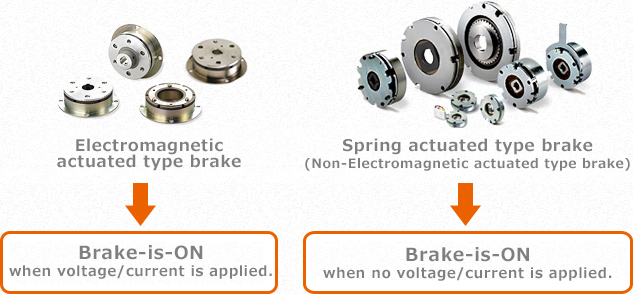
The systems for Miki Pulley’s electromagnetic brakes consist of electromagnetic actuated types and spring actuated types. The words of excitation and non-excitation are often used in the handling of electromagnetic brakes, but what do they mean? Excitation means that they work when energized. Conversely, non-excitation means that they work when not energized.
In other words, the brake is applied when energized for electromagnetic actuated type brakes and the brake is applied when not energized for spring actuated type brakes.
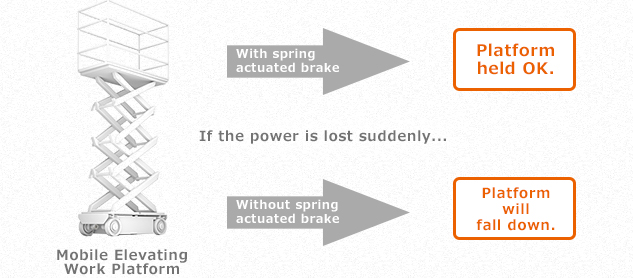
Spring actuated type brakes are mainly used for braking/maintaining during an emergency in machines or devices. For example, if energization is suddenly cut off due to the occurrence of an abnormality in an aerial work platform, the unit onto which articles are loaded (the bucket) may drop down without this brake. If a spring actuated type brake is mounted to the platform, it will play a role as a brake while the energization is cut off. Therefore, it is possible to maintain the bucket in that position.
> Miki Pulley's Electromagnetic Actuated Type clutch and brake product list
> Miki Pulley's Spring Actuated Type brake product list
Types of Electromagnetic Clutches
Miki Pulley’s electromagnetic clutches consist of friction type electromagnetic actuated type clutches and engagement type tooth clutches. The method with which each system generates torque is different.
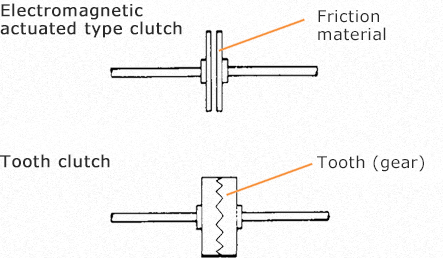
Electromagnetic actuated type clutches operate by generating transmission torque through pressing together friction materials. Tooth clutches generate transmission torque through the power of engaging gears called teeth. Accordingly, tooth clutches can generate larger torque than electromagnetic actuated type clutches.
> > Miki Pulley's Electromagnetic Actuated Type clutch and brake product list
> Miki Pulley's Electromagnetic Toothed Clutches product list
Structure and Operating Principles of Electromagnetic Clutches and Electromagnetic Brakes
We introduce the structure and operating principles of electromagnetic actuated type electromagnetic brakes, electromagnetic actuated type electromagnetic clutches and spring actuated type electromagnetic brakes below.
As we described in the types of electromagnetic clutches and brakes of Miki Pulley, excitation means that it works when energized. Conversely, non-excitation means it works when not energized.
In addition, electromagnetic actuated type clutches and electromagnetic actuated type brakes generate torque with the power of friction. However, spring actuated type brakes generate torque with the power of a spring. We have given these in an order that is easy to understand. Therefore, you will find it easier to understand if you read from the top.
INDEX
Structure and Operating Principles
of Electromagnetic Actuated Type Brakes
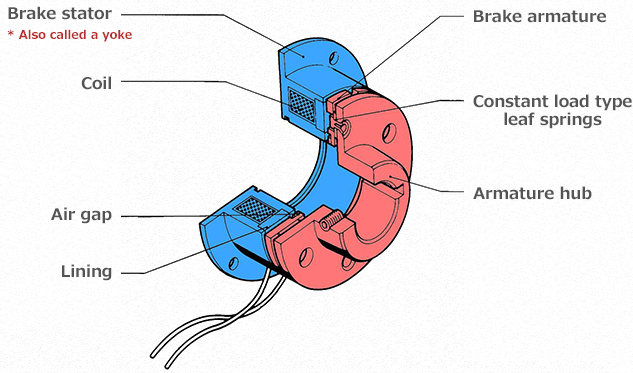
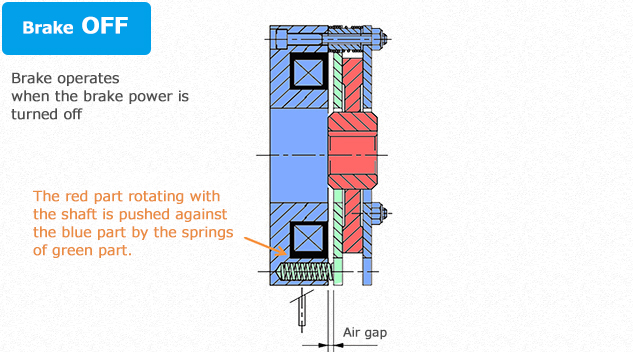
It is relatively easy to picture the structure and operating principles of electromagnetic actuated type brakes. Electromagnetic actuated type brakes consist of a movable part that moves together with the axis and a stationary part that is fixed to a wall or similar and does not move. In this figure, the red part moves and the blue part does not. There is a gap between these red and blue parts. This gap allows the red part to move.
Briefly, the red part that moves together with the axis is drawn close to the blue stationary part. This leads to the rotation of the axis coming to a stop due to the power of the friction (magnetic force). This plays the role of a brake.
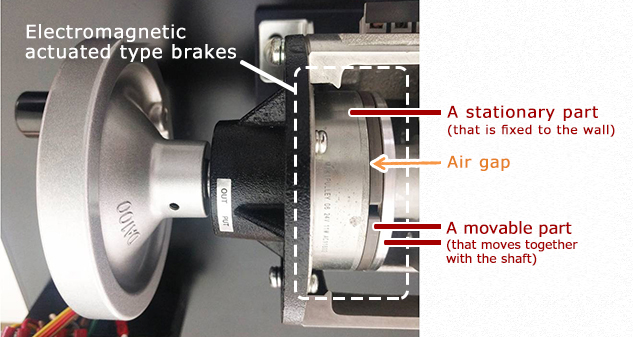
You can see what it is like from this actual photograph. When the brake is off, the handle on the left can turn around and around. However, when the brake is on, the moveable part that rotated together with the axis is drawn close toward the stationary part. This means it is no longer possible for the axis to rotate. Accordingly, the handle cannot turn.
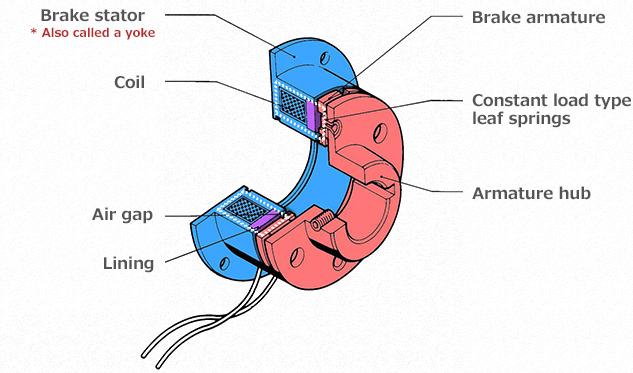 In short, it looks like this. Nevertheless, we explain about the operating principles in a little bit more detail below. It is easier to understand if you read it while looking at the figure above.
In short, it looks like this. Nevertheless, we explain about the operating principles in a little bit more detail below. It is easier to understand if you read it while looking at the figure above.
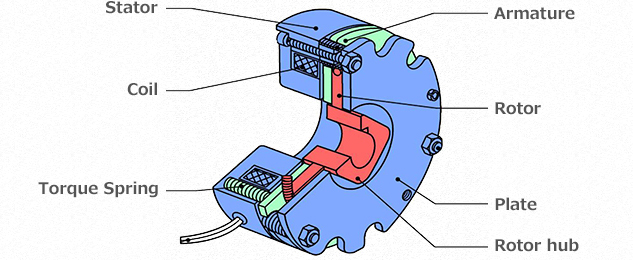
First, when the power to the brake is on, current flows through the coil. Thereupon, the brake stator around the coil plays a role like that of an electromagnet. The brake armature is then drawn toward the brake stator by the magnetic force. At this time, there is a part called the constant load type leaf spring between the armature hub and the brake armature of the moveable part. This constant load type leaf spring plays the role of a spring. Only the brake armature can move in the axial direction (in the direction with the brake stator). Thus, the brake armature stays close to the brake stator due to the magnetic force. A friction force is generated due to the friction materials called lining at this time. Braking then becomes possible.
When the power is turned off, this magnetic circuit disappears and the brake armature returns to its original location from after the leaf spring. The brake is then released.
> Miki Pulley's Electromagnetic Actuated Type clutch and brake product list
Structure and Operating Principles
of Electromagnetic Actuated Type Clutches
Next, we have electromagnetic actuated type clutches. It is difficult to picture the operating principles of the clutch, so we have made a movie. If you watch the movie, you will be able to see how the clutch moves to control the power.
We describe in detail the operating principles below.
Let’s look at an example of how the clutch operates to transmit power to the pulley unit in the image below.
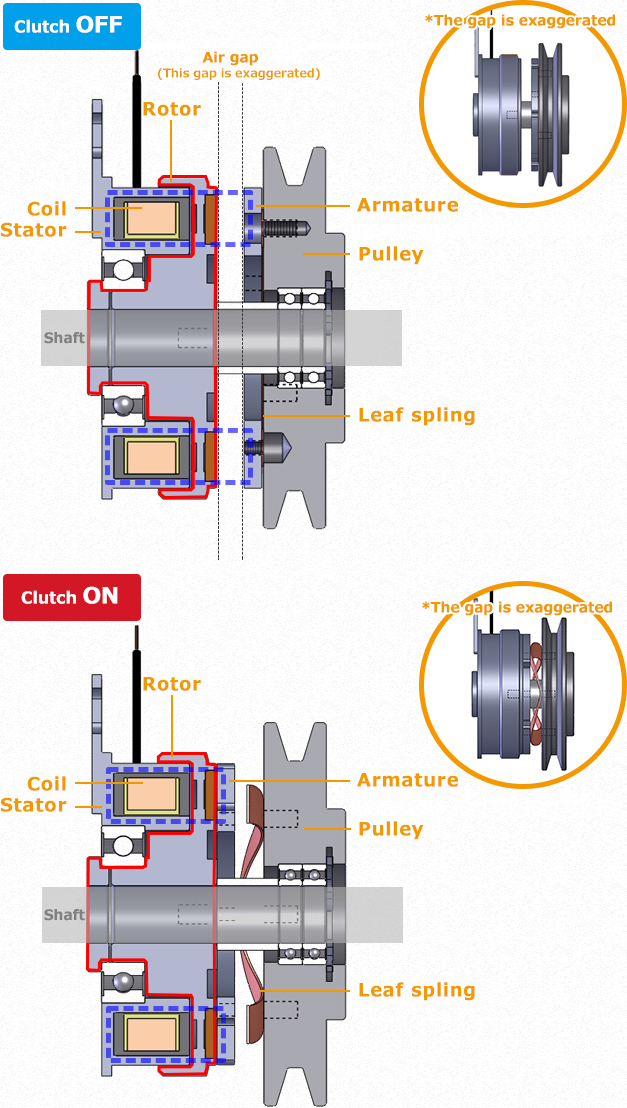
First, the part circled in red is called the rotor. This is the part that moves together with the axis. When the power is turned on, the coil built into this part called the stator is charged. The whole stator then plays a role like that of a magnet.
The magnetic force generated here passes through the rotor part and attracts the part called the armature. The rotating part in the red frame and the armature part come into close contact and the pulley becomes able to move.
When the power is turned off, the magnetic circuit disappears and the rotor loses its power to attract the armature. Furthermore, the armature returns to its original position due to the part called the leaf spring that is located between this pulley and the armature. In this way, the clutch is released and the transmission of power is cut off.
> Miki Pulley's Electromagnetic Actuated Type clutch and brake product list
Structure and Operating Principles of Spring Actuated Type Brakes
We have prepared a video that thoroughly shows the operating principles of spring actuated type brakes. If you watch it here, you will be able to better understand the movements of spring actuated type brakes.
We explain in further detail the operating principles of spring actuated type brakes below.
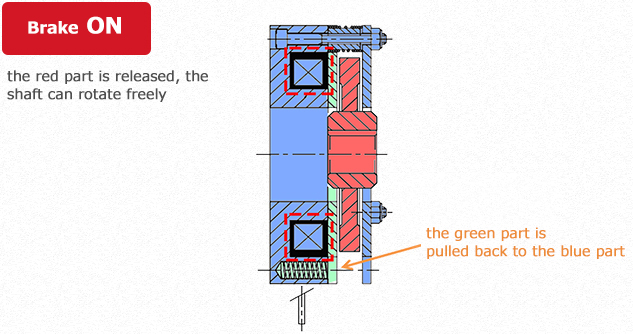
Unlike the electromagnetic actuated types we have described so far, spring actuated type brakes generate torque with the power of a spring. The operating principles are simpler than for electromagnetic actuated types.
In brief, the red part that rotates together with the axis is pushed up to the green part. This leads to it being pushed up to the blue stationary part and the rotation of the axis to come to a stop. This plays the role of a brake.
 日本語
日本語 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch 中文
中文 한국어
한국어






