What is a sensor? Our veteran engineer provides a simple explanation of the different types of sensor and gives some examples to illustrate the way they act as the sensory organs for a device.
What is a sensor?
Definition of sensor
Ms. Hama: Mr. Hashimoto! While learning about industrial robots, cobots, AGVs and AMRs, I noticed that they use “sensors”. Now I’d like to learn about the different types of sensors, the principles they use and what kind of applications in the industrial equipments.
Mr. Hashimoto: You’re very observant! Sensors play an important role in devices such as robots, AGVs, smartphones and drones. But let’s begin by defining what a sensor is. In the Japanese Industrial Standard “JIS-Z8103-2000”, a sensor is defined as follows.
• A series of elements in a measuring instrument or device that is directly affected by a measured amount. Note: This may be used to mean the same thing as “detector”. [Ref.] JIS standards https://kikakurui.com/z8/Z8103-2000-01.html
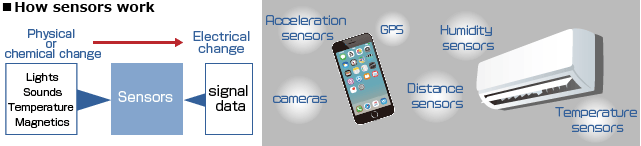
Mr. Hashimoto: A sensor is a device that converts physical or chemical phenomena, such as sound, light, heat or pressure, into electrical signals or data and then outputs those signals or data. Sensors are used in various situation of our daily lives. For instance, room air-conditioners have temperature and humidity sensors to measure the room’s temperature and humidity. Smartphones are equipped with GPS units that check the current location, acceleration sensors that detect tilt and movement, and distance sensors and cameras that measure distance.
What is the role played by sensors?
Ms. Hama: There are many different types of sensor. Could you give me some more detail about the roles played by each type?
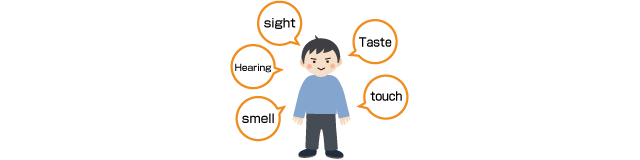
Mr. Hashimoto:People have various sensory organs that are associated with the five senses: sight, hearing, smell, touch and taste. Those organs are our “sensors”. Here is a table that shows the correspondence between the sensory organs of the human body, and the roles that sensors play in devices.
| Measurement of slope or rotations | Sensors that identify attitude or orientation by detecting the angles of rotating joints in robots, etc. |
|
|---|---|---|
Joints  |
potentiometers | Measures angular change within a certain range on a specific axis |
| Rotary encoders | Measures the angle or number of rotations for a rotating part on a specific axis | |
| Tilt Sensors | Measures slope in the location where the sensor is fixed | |
Balance  |
Acceleration sensors | Measures speed fluctuation per second |
| Gyro Sensors (gyroscope) | Measures angular velocity fluctuation per second | |
| Measurement of force or moment | Sensors that measure force or moment by the force fluctuation applied to a physical body | |
Force・Sense of touch  |
Strain gauges | Measures force or moment by displacement or deformation in an elastic body |
| Capacitive sensors | Detects change in a physical body using capacitance | |
| Piezoelectric elements | Detects force or pressure by the voltage generated when force is applied to a dielectric body (piezoelectric element, etc.) | |
| 6-axis force torque sensors | Measures force or moment by the changes in strain or capacitance | |
| Measurement of an object’s shape, color, position and movement | Sensors using camera that measure the distance to objects. In order to avoid collision with objects and sensor robot or AGV, such kind of sensors are equipped to obtain visual information like human. | |
Sense of sight |
Image sensors(Camera) | Uses the image captured by a camera to calculate data such as an object’s surface area, center of gravity, length and position and then output those data and measurements |
| Stereo vision | Accurately measures the distance to an object by capturing images from two cameras positioned in parallel | |
| Ultrasonic sensors | Measures the distance to an object by using ultrasonic waves | |
| Infrared distance sensors | Measures the distance to an object by using infrared light | |
| LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) | Uses light to measure the the distance & direction to the object | |
What types of sensor are there?
Ms. Hama: So, the roles of the five human senses are played by lots of different sensors in devices. Tell me more about the different sensors!
Mr. Hashimoto: OK, let’s take a closer look at 6 particularly important sensors out of those we’ve touched on so far.

Encoders

These are sensors that encode rotation angles and linear displacement. Those that detect rotation are called rotary encoders, and those that detect linear displacement are called linear encoders. Rotary encoders equipped a disk with even sp aced slits. Light from one side of the disk flashes through the slits and can be detected, measured from other side. Such results provide the rotation angle, number and speed information. These are widely used in equipment such as servomotors.
Acceleration sensors
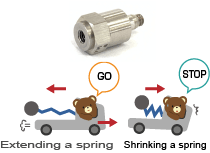
These are sensors that detect how much speed changes per second. There are various different types of acceleration sensor. But the simplest structure consist of a weight attached to the end of a spring. The sensor measures acceleration by the spring length fluctuation under the principal of inertia. The sensor measures acceleration by converting it to electrical signals. In recent years, small and low-cost sensors under MEMS technology are used in a wide range of applications.
■What is MEMS?
This is an acronym for Micro-Electromechanical System. It is a device with a microscopic structure that integrates sensors, actuators and electronic circuits fabricated by semiconductor technology. Because these devices are manufactured by semiconductor fabrication processes, they can integrate multiple functions onto a small, low-cost IC chip measuring just 1 square centimeter. Their applications include smartphones, computers, gaming machines and automobile sensors.
Ultrasonic sensors
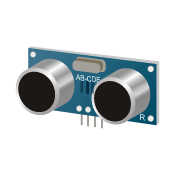
These are sensors that detect the distance to an object by measuring the time interval between transmission and reception. One widely method used for measuring distance is the ToF (time-of-flight) principle, which measures the time it takes for emitted light or sound to be reflected back from an object. Typical method is light or ultrasonic wave. Ultrasonic waves are emitted from the sensor head, reflect back from the object and are received by the sensor head.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
This is optical sensor technology that measures the distance to an object and identifies some nature of the object. LiDAR sensors scan & measure the beam dispersal or reflection by laser irradiation while moving. The measurement process also uses ToF. (ToF: time-of-flight). The Hayabusa also uses LiDAR to measure distance and calculated its landing point within just 1 meter tolerance, which is extremely accurate. These sensors are also used in cars and smartphones.
▶ Click Here For More Info
* Hayabusa(2) is a space probe which developed by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). It came back to the earth to bring sample in the asteroid (Ryugu) in winter of 2020.
Strain gauges

The sensor detect strain as an electrical signals. The resistance will increase or decrease depends on external force to expand or shrink the object.
So if strain gauge attached on the object, it will expand or shrink in portion to the object deformation to detect resistace fluctuation. Measuremet of force or moment will be available by detecting the elastic object deformation.
* Strain is the deformation amount of material when it expand or shrink in portion to the external force applied on.
Image sensors
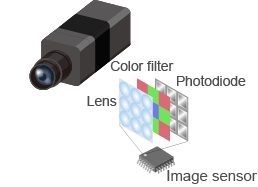
These sensors process data captured by a camera to output information such as the object’s position, angle, shape, dimensions and quantity, and then compares those data with recorded data to determine validity. They use semiconductor elements to convert light to electrical signals. It is equivalent to the retina in a human eye. They consist of multiple layers with color filters (RGB) inserted between micro-lenses and photodiodes to allow them to capture color image signals.
Where are sensors used?
Ms. Hama: So, sensors are really useful in all the situation of daily life, aren’t they?
Mr. Hashimoto:There are still lots more examples of applications in daily life. There are image sensors and sound sensors in the intercoms we use for getting into buildings. The optical sensors detect visitor to turn on outside light automatically at night. And there are lots of other examples I could talk about, such as our smartphones, which have GPS units for location information and gyroscopic sensors to counter camera shake.
Ms. Hama: I think we should be more aware of places where sensors are used. Do you have any examples of sensors used in devices or machine components?
Mr. Hashimoto: Of course! Let me show you two examples of Miki Pulley products.
Torque sensors × Couplings
This sensor detects the torque generated when the device is rotated. A capacitive-type torque sensor converts the displacement of two metal plates built-in capacitor to torque and displays the results. Capacitor is an ordinary passive component that either stores or release electrical charge according to its capacitance. It is made up of derivative in between 2 metal plates. MP is developing built-in capacitive type torque sensor couplings. It is possible to detect load torque on coupling as well as transmit rotation. This coupling make it possible to grasp the machine operation status correctly. Compared with system mainly consist of torque measurement tools, it is possible to make system more simple by reducing many components.
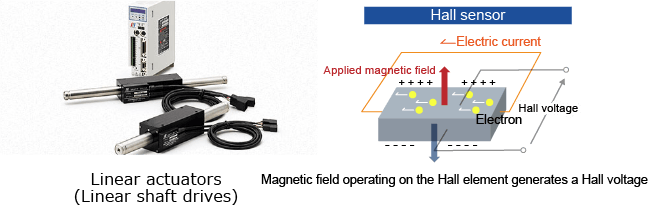
Magnetic sensors × Linear actuators (Linear shaft drives)
These are magnetic sensors that detect the magnitude and direction of geomagnetism and the magnetism generated by magnets and electrical current. Miki Pulley linear actuators (linear shaft drives) use Hall elements to detect location information. Because the location can be detected using the magnetic flux generated by the shaft, they can operate without an external location sensor. Also, because the built-in location sensor directly detects the position of the magnetic pole, driving force is generated immediately after startup without the need to provide an external magnetic pole detector. Functions such as positioning operations are built into the driver, allowing relatively complex positioning operations without an external controller.
Ms. Hama: OK, now I see how sensors are also used in devices and machine components! I often hear people talking about how sensors are useful in predictive maintenance. I definitely need to spend more time learning about sensors so that I can use them in design and development technology!


Mr. Hashimoto, Miki Pulley Co., Ltd
Joined Miki Pulley in 1972. Worked as a Product Manager in the Marketing and Technology divisions in positions both in Japan and overseas. He has also been involved with other organizations through joint research projects with universities and specialist bodies. He currently works as technical adviser and staff trainer.

 日本語
日本語 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch 中文
中文 한국어
한국어





